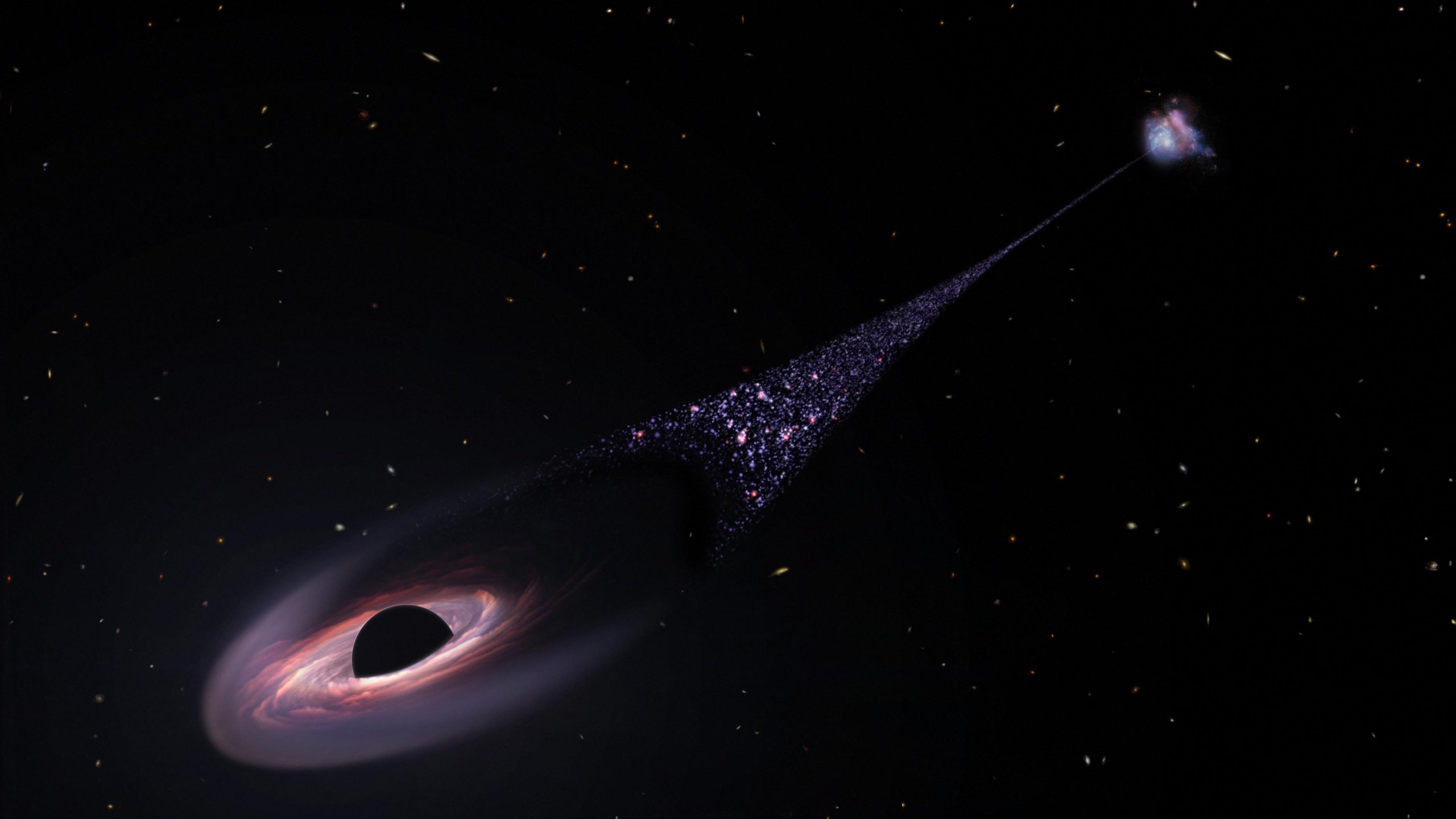
Esta é a impressão artística de um buraco negro supermassivo em fuga. Pesquisadores do IAC descobriram que uma estrutura extraordinariamente fina de estrelas pode na verdade ser uma galáxia vista da borda, em vez de um rastro deixado por um buraco negro descontrolado. Crédito: NASA, ESA, Leah Hostack (STScI)
Um estudo realizado por uma equipa de investigadores do Instituto de Astrofísica das Canárias (IAC) mostrou que a estrutura de estrelas invulgarmente finas, recentemente descobertas por[{” attribute=””>Hubble Space Telescope, could be a galaxy seen edge-on. This finding goes against the original interpretation in which a fleeing supermassive black hole was leaving a trail of stars in its wake. The new interpretation is published in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics Letters.
A mysterious trail of stars formed eight thousand million years ago and recently discovered by the Hubble Space Telescope has been a challenge to a number of research groups. Its size is similar to that of the Milky Way, and this very long narrow structure has given rise to several explanations of its origin.

Above: Image of the object observed with the Hubble Space Telescope. It shows the emission in the ultraviolet part of the spectrum. Middle: Ultraviolet image of a local galaxy without a bulge and observed edge-on (IC 5249). The similarities are obvious. Bottom: The same galaxy IC 5249 observed in the visible part of the spectrum. The spatial scales of the three images are identical. Credit: HST
According to a controversial initial hypothesis, this trail of stars could be the result of the passage of a supermassive black hole through a huge cloud of gas. This idea quickly fired the imagination of the astronomical community, because it needs a large set of complex exceptional circumstances. For this reason, several scientific teams have continued to explore different, and less exotic scenarios which can explain the observations.
In a recent study, researchers at the IAC have reached the conclusion that this unusual structure of stars could be interpreted as a galaxy without a bulge seen edge-on. This type of galaxies, also called thin, or flat galaxies, are relatively common. “The motions, the size, and the quantity of stars fits what has been seen in galaxies within the local universe” explains Jorge Sanchez Almeida, an IAC researcher who is the first author of the article. “It’s a relief to have found the solution to this mystery, the new proposed scenario is much simpler. In one sense it is also a pity, because the existence of fleeing black holes is expected, and this could have been the first one to be observed.”

Comparison between this “object” and an edge-on galaxy in the local Universe (IC5249): images (a and b) the intensity along the track (c and d) and its rotational velocity (e). This object and IC5249 turn out to be extremely similar in all their physical parameters, which supports the idea that the “object” is really an edge-on galaxy. Credit: IAC
To support the hypothesis of the interpretation in terms of a galaxy, the team compared the mysterious structure with a well-known local galaxy without a bulge, IC5249, which has a similar mass of stars, and found surprising agreement. In the words of Mireia Montes, an IAC researcher who is a co-author of the article, “When we analyzed the velocities of this distant structure of stars we realized that they were very similar to those obtained from the rotation of galaxies, so we decided to compare a much closer galaxy, and found that they are extraordinarily similar.”

Relation between the rotation velocity of a galaxy and its stellar mass (grey dots). This is the well known Tully Fisher relation, which characterizes galaxies, (which is basic for measuring the distances to galaxies from their observed rotation velocities and apparent luminosities). The object lies just on the relation, as would be expected for any disc galaxy. Credit: IAC
“We also looked at the relation between the mass of the assumed galaxy and its máximum velocity of rotation, and discovered that indeed it is a galaxy which behaves like a galaxy,” states Ignacio Trujillo, an IAC researcher who has taken part in the study. “It is an interesting object, because it is quite a large galaxy at a very large distance from Earth, where the majority of the galaxies are smaller,” he adds.
Upcoming observations will allow the study of this object in greater detail.
Reference: “Supermassive black hole wake or bulgeless edge-on galaxy?” by Jorge Sánchez Almeida, Mireia Montes and Ignacio Trujillo, Sccepted, Astronomy and Astrophysics Letters.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202346430

“Aficionado por música. Jogador. Praticante de álcool. Leitor profissional. Estudioso da web.”